
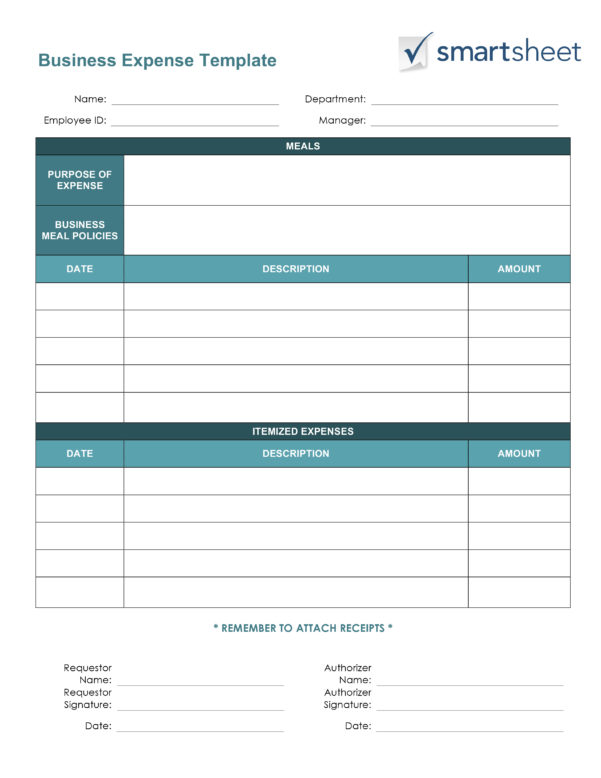
The most common type of legal entity for a self-employed independent contractor to form is an LLC. LLC is short for Limited Liability Company. An LLC is the simplest of all formal legal entities. However, the most common type of independent legal entity that a self-employed independent contractor forms is an LLC. Each of them has different attributes and tax structures.
There are a variety of different types of corporations in the United States. The formal definition of a corporation is a legal entity that is separate and distinct from its owners. In this article, we answer whether a self-employed independent contractor should form a company, if they need to, or are required to incorporate, and how they would work for their own corporation. When you’re an unincorporated self-employed independent contractor (also known as a sole proprietor) everything-your income, expenses, and liabilities-gets funneled through your own personal bank account. However, that doesn’t mean they’ve formed their own company, such as an LLC or corporation. However, sometimes independent contractors get confused and wonder if they should form an actual legal corporate entity, or rather an official business.Ĭolloquially, self-employed and independent contractors call themselves small business owners.
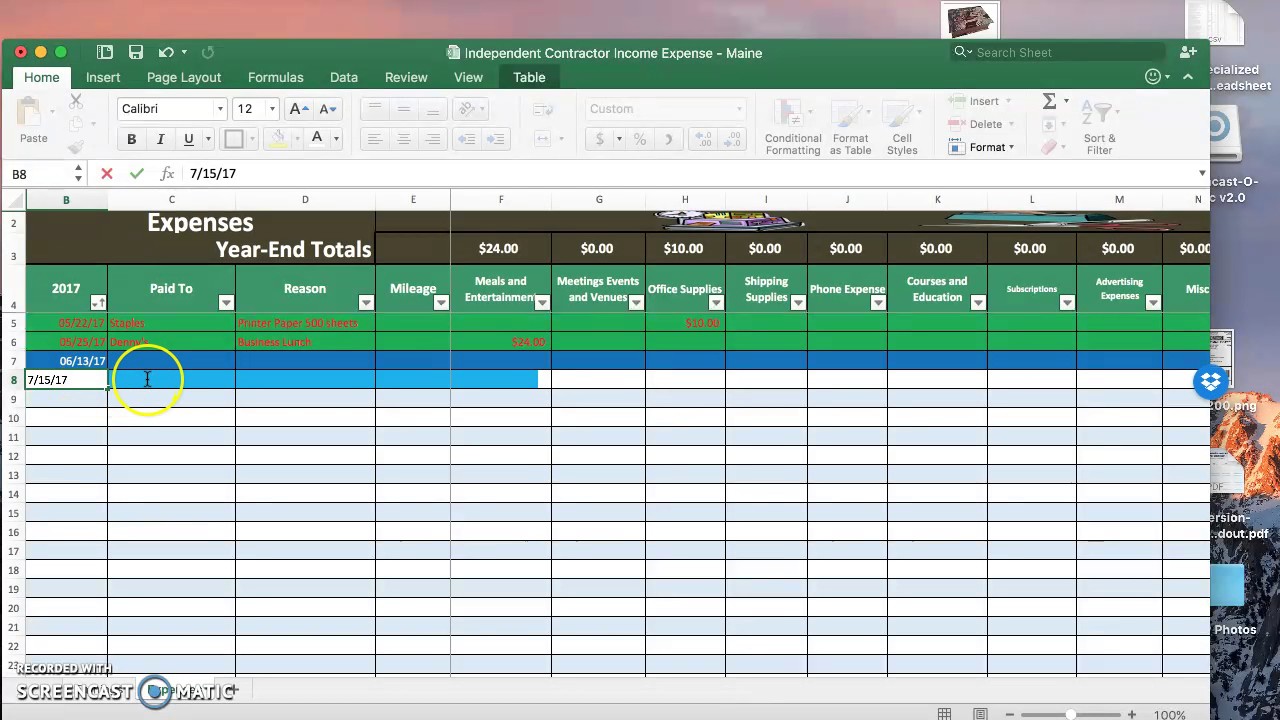
Typically, when you think of an independent contractor, a gig worker, or someone who is self-employed you think of somebody that works for themselves. As the gig economy expands and more people work as independent contractors you’re probably asking, can I be an independent contractor for my own corporation?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
